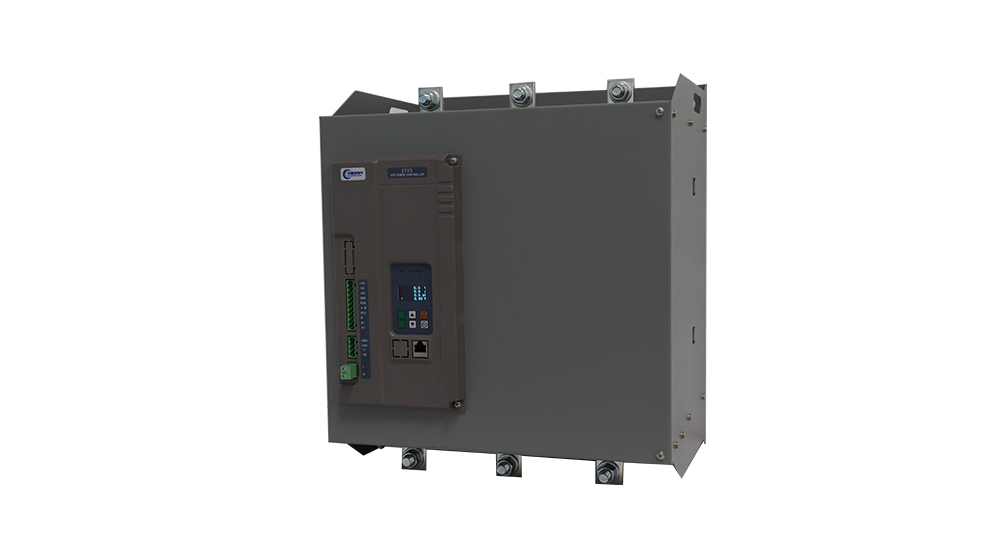
When there is a problem with your power regulator, here are some general inspection steps to help you identify and solve the problem:
Check power supply and connections:
Ensure that the voltage and frequency of the input power supply are within the specified range.
Check cable connections and plugs to make sure they are not loose or damaged.
Alarms and Indicators:
Check the equipment for alarm or fault lights, which may provide clues about the problem.
Output current and voltage:
Use appropriate test tools to measure the output current and voltage of the power regulator to ensure they meet the expected values.
Loading issues:
Make sure there are no faults or short circuits in the load connected to the power regulator.
Check whether the load current is within the specified range.
Temperature and cooling:
Check the temperature of the power regulator to make sure it is not overheating.
Ensure that the cooling system is operating normally and there are no clogging or lack of heat dissipation problems.
Control parameters:
Check the control parameters of the power regulator, such as output voltage, frequency, overcurrent maintenance and other settings, to ensure they are configured correctly.
Maintenance functions:
If the power regulator has protection functions (such as overload, overheating, short-circuit protection), check whether there are conditions that may trigger these protection functions.
Circuit Boards and Components:
Check the circuit boards and components inside the power regulator to ensure that they are not visually damaged or burned out.
Power regulator manual:
Refer to the power regulator's user manual or technical specification sheet for specific suggestions on troubleshooting.