The specific difference between power regulator and thyristor voltage regulator
Currently, in the field of AC power supply, there are two basic control methods for thyristors: power adjustment (adjustment of power P) and voltage adjustment (adjustment of voltage V). The corresponding products are called: power regulator and voltage regulator. Adjustment Work and voltage regulation are two different concepts, and they are also different in use.
The power regulator is also called a cycle number controller. The thyristor is turned on at the zero crossing point of the voltage (or current) and is also cut off at the zero crossing point of the voltage (or current), so the output waveform is a complete sine wave. If you set a A fixed time period T, within this period, by controlling the on-time TON and the off-time TOFF, the purpose of controlling the output cycle number (conduction rate) can be achieved.
The thyristor voltage regulator achieves the purpose of changing the voltage by controlling the phase shift angle. Therefore, the output end is a phase-shifted missing-angle wave.
Because the output voltage of the voltage regulator is a missing-angle sine wave and contains high-order harmonics, if no measures are taken, it will cause certain pollution to the power grid, which may have adverse effects on electrical appliances on the same grid.
As a thyristor power switching device, the power regulator is widely used in electric heating applications because of its good controllability, economy and durability.
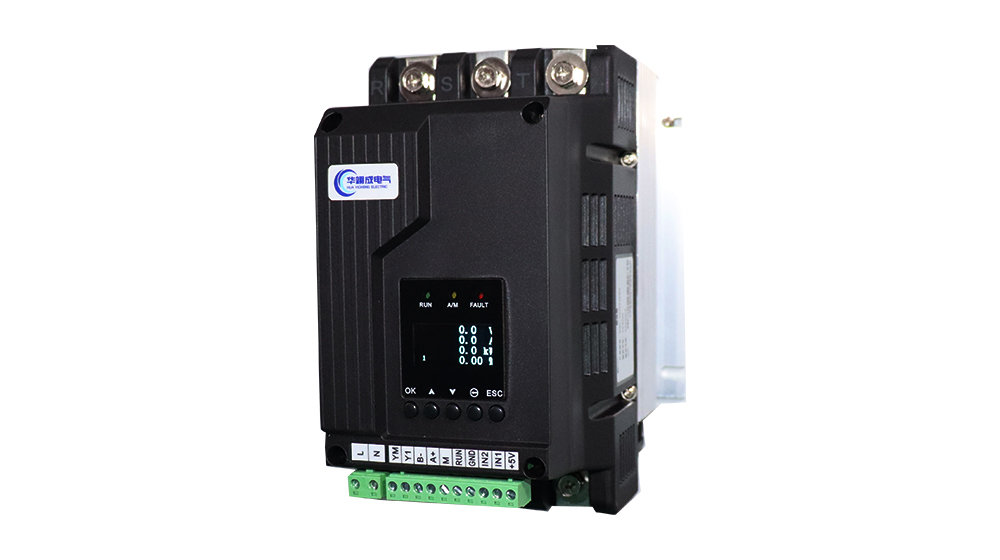
The 3-phase power regulator is composed of a trigger plate, a special radiator, a fan, a casing, etc. The core part uses a 0 control board and a thyristor module; the heat dissipation system uses a high-efficiency heat dissipation and low-noise fan. The whole machine has all the functions of the control board .The current capacity of the complete machine has 7 levels from 40A to 800A.
The 3-phase thyristor power regulating voltage regulator uses a digital circuit to trigger the thyristor to realize voltage regulation and power regulation. The voltage regulation adopts the phase-shift control method, and the power regulation has two methods: fixed period power adjustment and variable period power adjustment. The control board has phase-locked loop synchronization circuit, automatic phase determination, phase loss maintenance, power-on soft start, slow shutdown, radiator over-temperature detection, constant current output, current restriction, over-current maintenance, serial working status indication and other functions .